Advertisement
Identifying Causes of Loose Stools
Advertisement
Loose stools or diarrhea, characterized by bloating, gas, and watery or soft bowel movements, can be an uncomfortable issue. While occasional loose stools might be due to simple factors like eating greasy or spicy food, or drinking alcohol, recurring instances might indicate a more serious condition, ranging from viral infections to chronic digestive disorders. Prolonged bouts of diarrhea can lead to dehydration and other health complications.
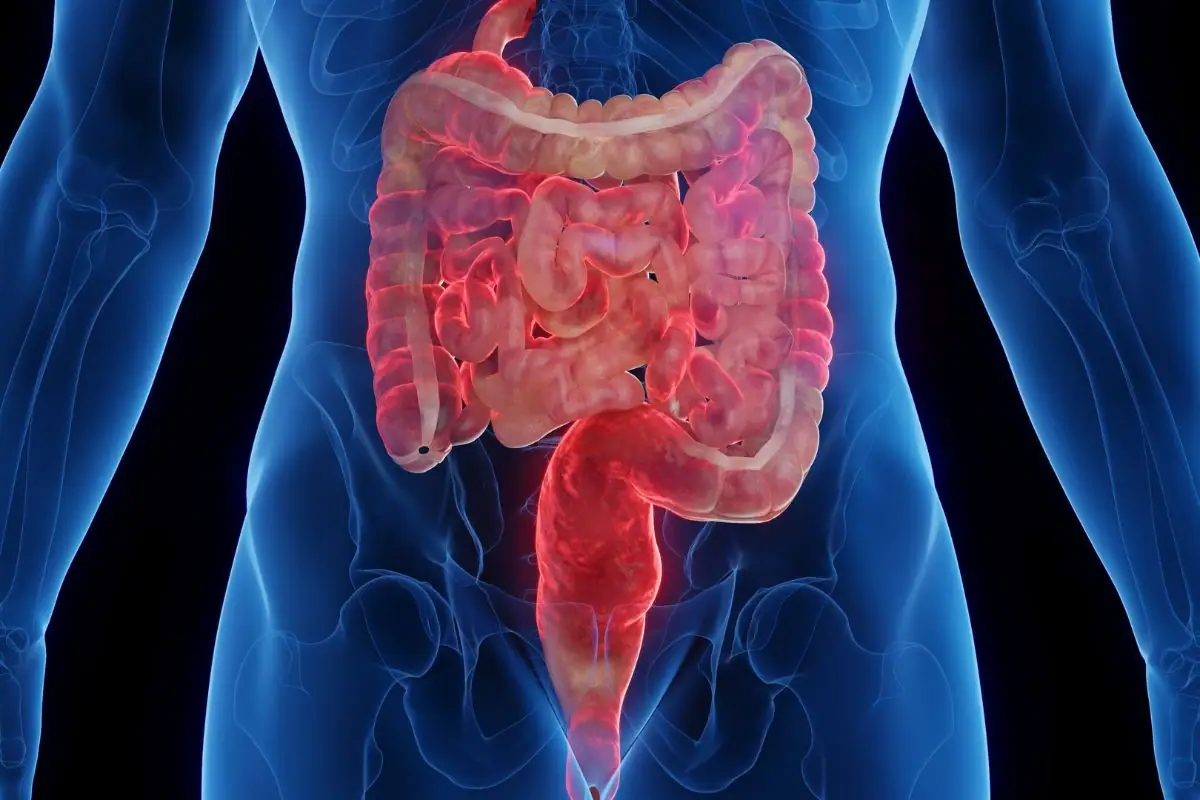
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease is a chronic auto immune disorder that inflames the digestive system's lining, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue, bloating, and sometimes blood in the stool. While it shares similarities with ulcerative colitis, both the causes and treatment approaches for Crohn's can differ significantly.
Advertisement
Bile Acid Malabsorption
Bile is produced by the liver and is very useful in aiding digestion, it helps to break down food into nutrients which are later absorbed and distributed all over the body. Some chronic diseases can cause progressive harm to both the liver and gallbladder thus affecting the production of bile— impeding its function and stopping fat breakdown at the intestines. Gallstones, Liver Cirrhosis, as examples of conditions demonstrating this issue. Similarly, absence of appropriate absorption of bile acid results in diarrhea or loose stools.

Advertisement
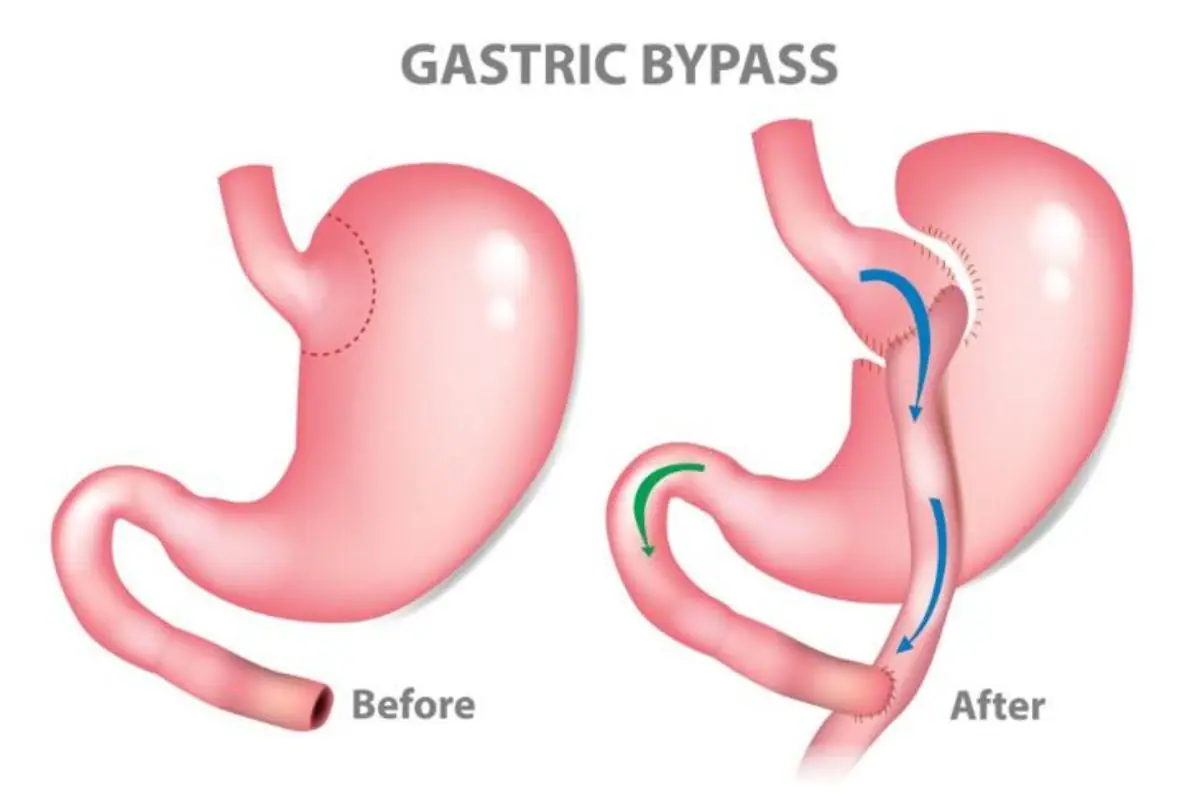
Dumping Syndrome
Dumping syndrome often occurs in individuals who have undergone weight loss surgery, such as gastric bypass or gastric sleeve. The surgically altered digestive system may struggle to handle certain foods, particularly refined sugars and high-fat items. This inability to digest effectively leads to food moving too quickly through the gut, causing symptoms like cramps, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Advertisement
Dietary Changes
One of the most common triggers for loose stools is dietary. Foods that some people struggle to digest, such as lactose, gluten, or certain sugars found in alcohol, can lead to diarrhea. These sugars are also prevalent in fruits, vegetables, and artificial flavorings. Additionally, fatty and spicy foods can cause the gut to produce excess mucus, speeding up digestion and resulting in softer stools.

Advertisement
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a prevalent condition that leads to recurrent symptoms including diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, bloating, and gas. These symptoms are often worsened by stress, poor diet, and alcohol consumption. For those with IBS, adopting a diet with mild foods, limiting fast food and dairy intake, and managing stress through therapy or mindfulness practices can significantly alleviate symptoms.
Advertisement
Chronic Diseases and Conditions
Several chronic diseases and conditions can cause ongoing issues with diarrhea. For example, diabetes can impact digestive health due to the nerve damage that occurs with long-term high blood sugar, leading to a condition known as diabetic neuropathy which affects gut motility. Similarly, hyperthyroidism speeds up the body’s metabolic processes, including digestion, often resulting in diarrhea. Managing these underlying conditions with appropriate medical supervision is crucial to controlling their gastrointestinal symptoms.

Advertisement
Post-Gallbladder Removal
Individuals who have had their gallbladder removed may experience changes in bile flow, which can affect fat digestion. Without the gallbladder acting as a reservoir, bile flows directly into the intestines, sometimes leading to diarrhea, particularly after eating fatty meals. Adjusting the diet to include smaller, more frequent meals and reducing fat intake can help manage diarrhea in individuals without a gallbladder.

Advertisement
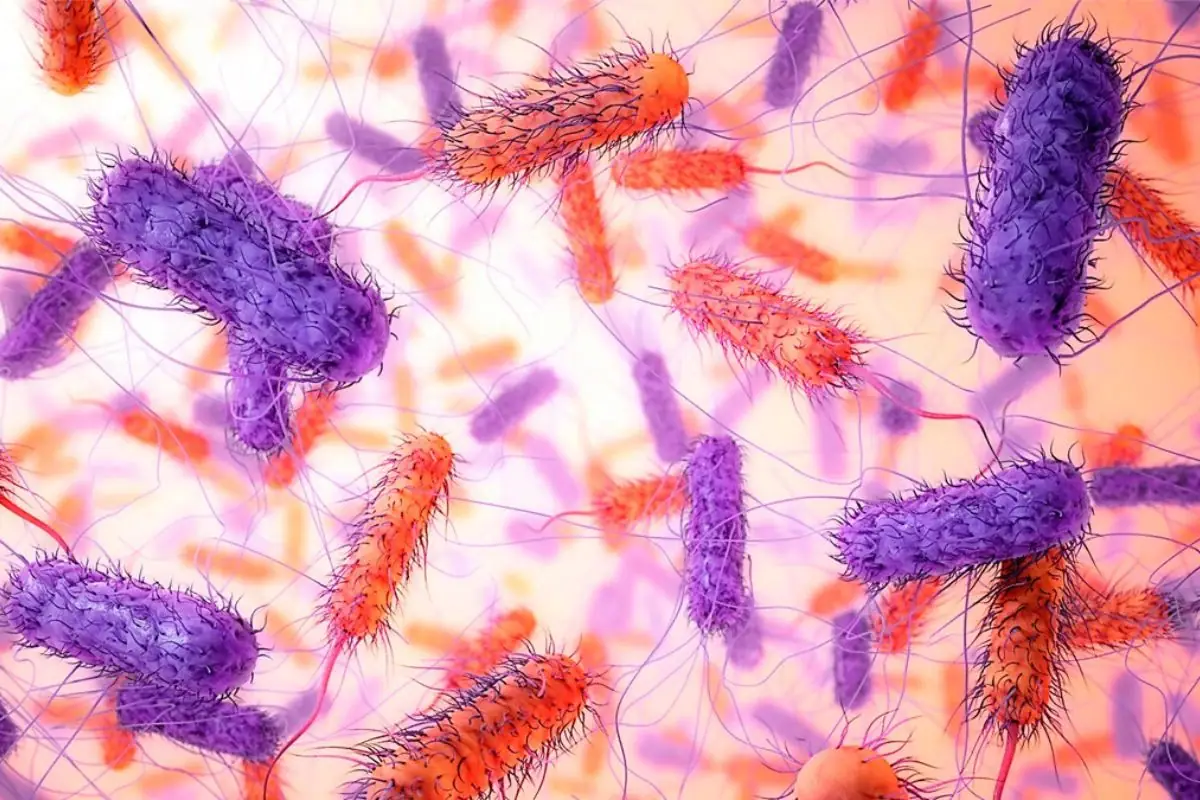
Infections
Viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections are prominent triggers for diarrhea. Viruses like norovirus or rotavirus, bacteria such as E.coli or salmonella, and parasites like giardia can invade the digestive system and cause severe inflammation and diarrhea. These infections often result in watery stools, accompanied by symptoms like fever and vomiting, and are particularly common in areas with poor sanitation or during travel to certain countries.
Advertisement
Celiac disease
Celiac disease leads to an intense immune reaction to gluten, which is present in wheat and several other foods. People with this condition typically suffer from diarrhea or loose stools after consuming gluten. There are also less severe types of gluten intolerance, such as non-celiac gluten sensitivity, which can similarly cause diarrhea and other gastrointestinal discomforts.
Advertisement
Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
Conditions such as functional diarrhea, where there is chronic diarrhea without a clear cause, fall under functional gastrointestinal disorders. These are diagnosed after ruling out other causes like infections, allergies, and chronic diseases. Stress and psychological factors can exacerbate these conditions, making management often multifaceted, involving dietary changes, stress relief practices, and sometimes medication.
.png)




