Advertisement
Corn's Hidden Health Treasures Revealed
Advertisement
Adhering to a nutritious diet is simpler than often perceived, with experts advising to limit intake of starchy, overly processed foods and those laden with sugar. Instead, a diet rich in high-fiber grains, fruits, nuts, yogurts, and vegetables is recommended. Among these, corn stands out, yet its health benefits frequently elude common understanding. Despite being one of the most consumed vegetables in North America and China, the full extent of corn's nutritional advantages remains largely underappreciated and often misrepresented.
The Dual Nature of Corn: Grain and Vegetable
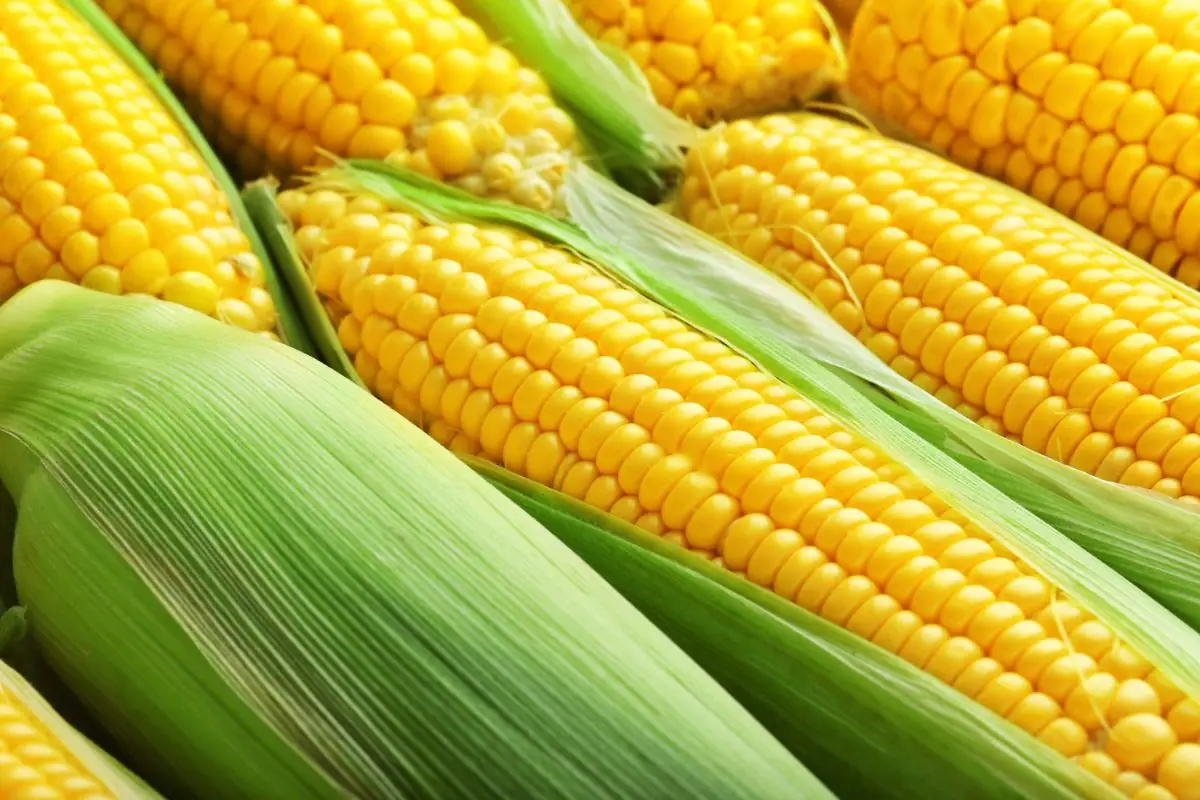
Corn's classification as either a grain or a vegetable is determined by its harvest time. The USDA states that young, soft-kernel corn is a vegetable, while mature corn is classified as a grain. Sweet corn, which makes up a small fraction of total corn consumption, is considered a vegetable. In contrast, corn used in products like cornbread and polenta is viewed as a grain. This distinction is important for understanding corn's versatility in the diet.

Advertisement
Corn's Protein Content: Surprisingly High
Corn is an unexpectedly rich source of protein, with one cup providing nearly five grams. This amount surpasses the protein content in an equivalent serving of broccoli. Although corn's plant-based protein is incomplete—lacking some essential amino acids—combining it with other foods can help the body assemble a complete protein profile, essential for health and well-being.

Advertisement
Beneficial Fiber in Corn
Corn is a fiber-rich food, offering more than three grams per cup. This fiber is not only beneficial for digestive health, aiding in smooth digestion, but it also plays a role in reducing the risk of chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. Consuming corn can help individuals meet the USDA's daily fiber intake recommendations and promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria.

Advertisement
The Starch in Corn: A Double-Edged Sword
Corn contains nine grams of carbohydrates per cup, including natural sugars, making it a starchy vegetable. This has led some diet experts to caution against its consumption due to potential weight gain. However, corn's carbohydrates are absorbed gradually, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar levels. The starch in corn is also resistant, digesting slowly and providing a lasting sense of fullness.

Advertisement
Antioxidant-Rich Corn for Health Protection
Corn stands out among common grains for its high total antioxidant activity, attributable to its rich phytochemical content. These compounds, including flavonoids and carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin, offer a range of health benefits. They possess powerful antioxidant properties that can reduce the risk of various cancers and chronic diseases, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, while also promoting eye health.

Advertisement
Corn and Heart Health: A Closer Look
Corn consumption has been linked to improved heart health. Its high fiber content can help lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, the phytochemicals in corn contribute to cardiovascular protection, making it a heart-healthy choice for those looking to maintain or improve their heart health through diet.

Advertisement
Corn's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Despite concerns about its starch content, corn can have a positive effect on blood sugar regulation. Its high fiber content slows the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, helping to manage blood sugar levels. This makes corn a suitable option for individuals with diabetes, as part of a balanced diet, to enjoy without causing significant blood sugar spikes.
Advertisement
Corn as a Source of Essential Minerals
Corn is not only nutritious in terms of vitamins and protein but also provides essential minerals such as zinc, magnesium, and iron. These minerals are vital for various bodily functions, including bone health, energy production, and overall physical well-being. Incorporating corn into the diet can help ensure adequate intake of these important nutrients.

Advertisement
Supporting Immune Health with Corn
The nutritional profile of corn, rich in antioxidants and vitamins, plays a significant role in supporting the immune system. These nutrients help protect the body against infections and diseases by strengthening the immune response. Regular consumption of corn can contribute to a robust immune system, aiding in the maintenance of good health.

Advertisement
Corn's Role in Mental Health
Corn contains folate and vitamin B6, nutrients essential for the production of neurotransmitters in the brain. These neurotransmitters are crucial for regulating mood and cognitive functions. Including corn in the diet can thus have a positive impact on mental health, improving mood and supporting brain health.

Advertisement
Sustainable Eating with Corn
Corn's versatility and nutritional benefits make it an excellent choice for those seeking to adopt a sustainable and health-conscious diet. Its ability to be used in various culinary applications, combined with its environmental benefits as a crop, underscores its value in promoting a healthy, sustainable dietary pattern.

.png)




