Advertisement
Is It Celiac Disease? Spot the Warning Signs
Advertisement
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that, due to genetic predisposition, affects some individuals. It primarily involves the small intestine and usually disrupts the digestive process; however, it can cause many symptoms. People with celiac disease cannot tolerate gliadin, a gluten protein found in grains like wheat, barley, rye, and some oats. Unfortunately, the symptoms are hard to recognize and may be confused with less serious conditions such as indigestion. To make matters worse, if not managed appropriately, celiac disease can make the body vulnerable to other diseases, including type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, anemia, osteoporosis, infertility, epilepsy, migraines, and, in extreme cases, intestinal cancer. Since there's no cure for celiac disease, the only way to manage the condition is to adopt a gluten-free diet.
Loose Bowel Movements
People with celiac disease often experience chronic loose bowel movements unless they switch to a gluten-free diet. Their stools may be pale, watery, and malodorous. Because the body doesn't tolerate gluten, it may not absorb fat, iron, and other nutrients from food as well as it should. Consequently, someone with this condition might become accustomed to passing loose stools and not realize they have the disease. This delay, unfortunately, tends to cause complications later on.

Advertisement
Abdominal Bloating
Celiac patients also complain of bloating and abdominal fullness, another byproduct of the impaired digestive process. Impaired digestion leads to the buildup of gases and fluids, mostly in the small intestine. Consequently, the abdominal pressure produced may cause cramping, pain, and, in some cases, nausea. Many people attempt to use over-the-counter medications to alleviate these symptoms; however, this is only a temporary fix.

Advertisement
Flatulence
About 50 percent of people with celiac disease report chronic flatulence. When their small intestine is unable to absorb gluten-rich food properly, sugars like maltose, lactose, and sucrose pass into the colon. There, they ferment and produce hydrogen, which is expelled through the rectum as gas. This symptom can be both uncomfortable and embarrassing. However, like other symptoms of celiac disease, it may not raise any alarm bells. A person with undiagnosed celiac may assume they are more gassy than others and not investigate their symptoms further.

Advertisement
Acid Reflux and Heartburn
Though not a classic symptom of celiac disease, many patients experience acid reflux and heartburn. It feels like a burning sensation rising in the chest due to acid from the stomach moving up past the lower esophageal sphincter. Interestingly, patients tend to experience much relief from acid reflux once they eliminate gluten from their diet.
Advertisement
Constipation
Although the most distinctive sign of celiac disease is loose bowel movements, about 15 percent of people experience constipation. This happens when undigested, unabsorbed food forms stool in the lower end of the small intestine, and the body is only able to absorb moisture from it. Consequently, this results in dry, hard stool that may be difficult to pass. People with this symptom often do not respond to laxatives, which is a telling sign of a larger problem.

Advertisement
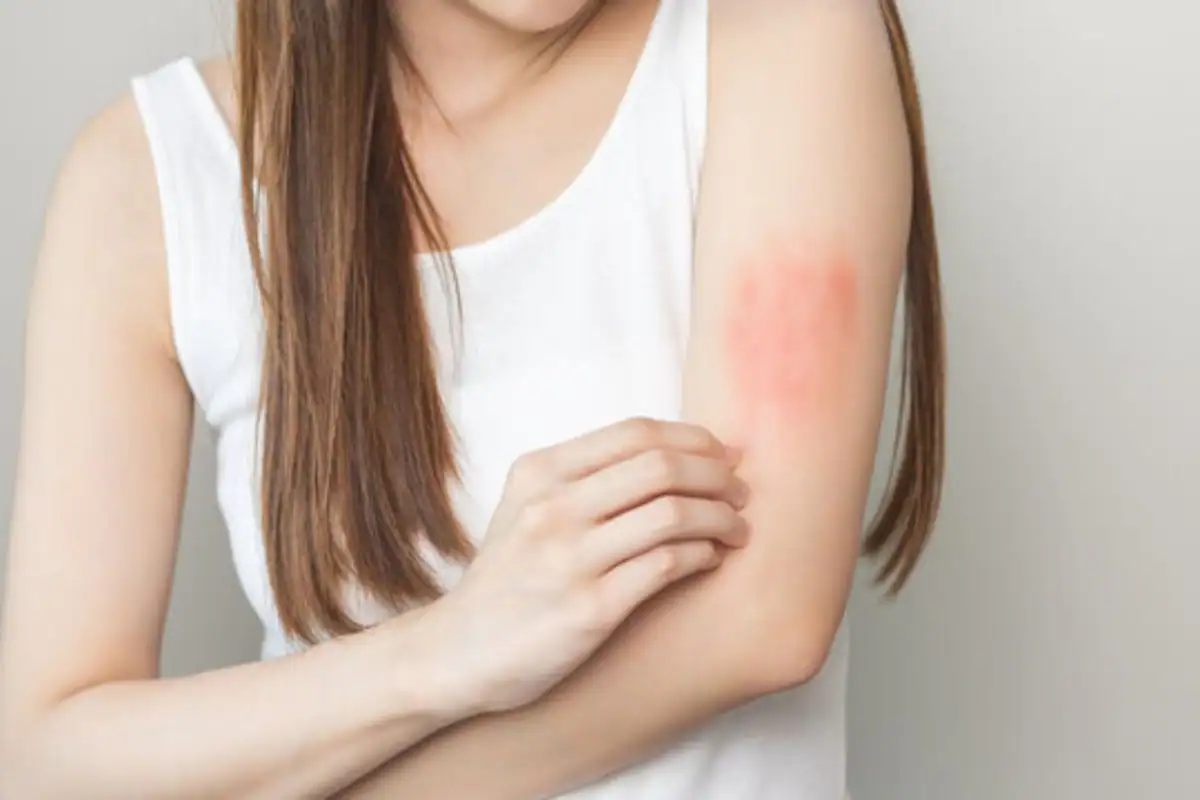
Skin Rash
A type of skin rash called dermatitis herpetiformis (DH), though not a symptom of celiac disease per se, often occurs in individuals with it and is triggered by gluten intolerance. This condition is characterized by blisters, usually on the knees, elbows, or buttocks, and is often itchy. If a person develops a DH rash alongside other celiac disease symptoms, they should talk to their doctor.

Advertisement
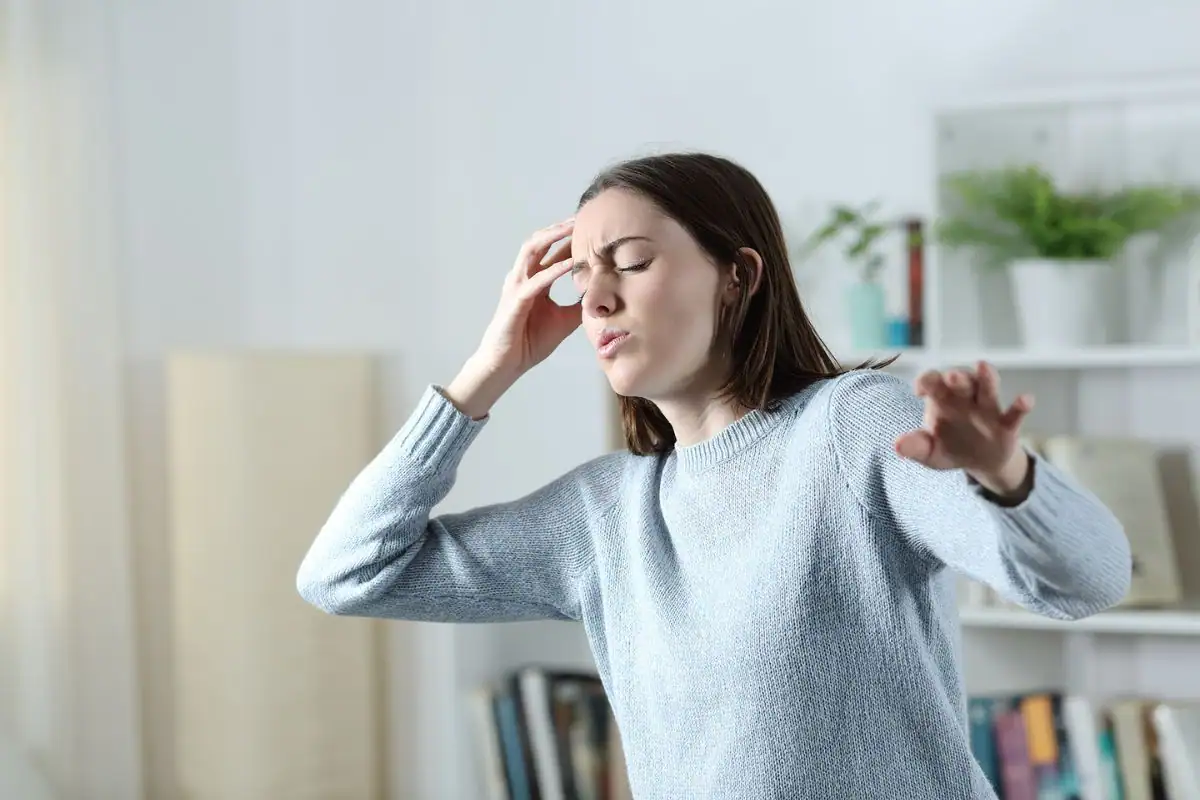
Weakness and Fainting Spells
Celiac disease impairs the digestive process and leads to malabsorption of nutrients from food. Vital substances like iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12 cannot be absorbed, potentially causing anemia. As a result, people with celiac disease may feel weak, lack energy, and experience fainting spells. Anyone who eats a healthy, balanced diet but has anemia should consult a doctor about testing for celiac disease.

Advertisement
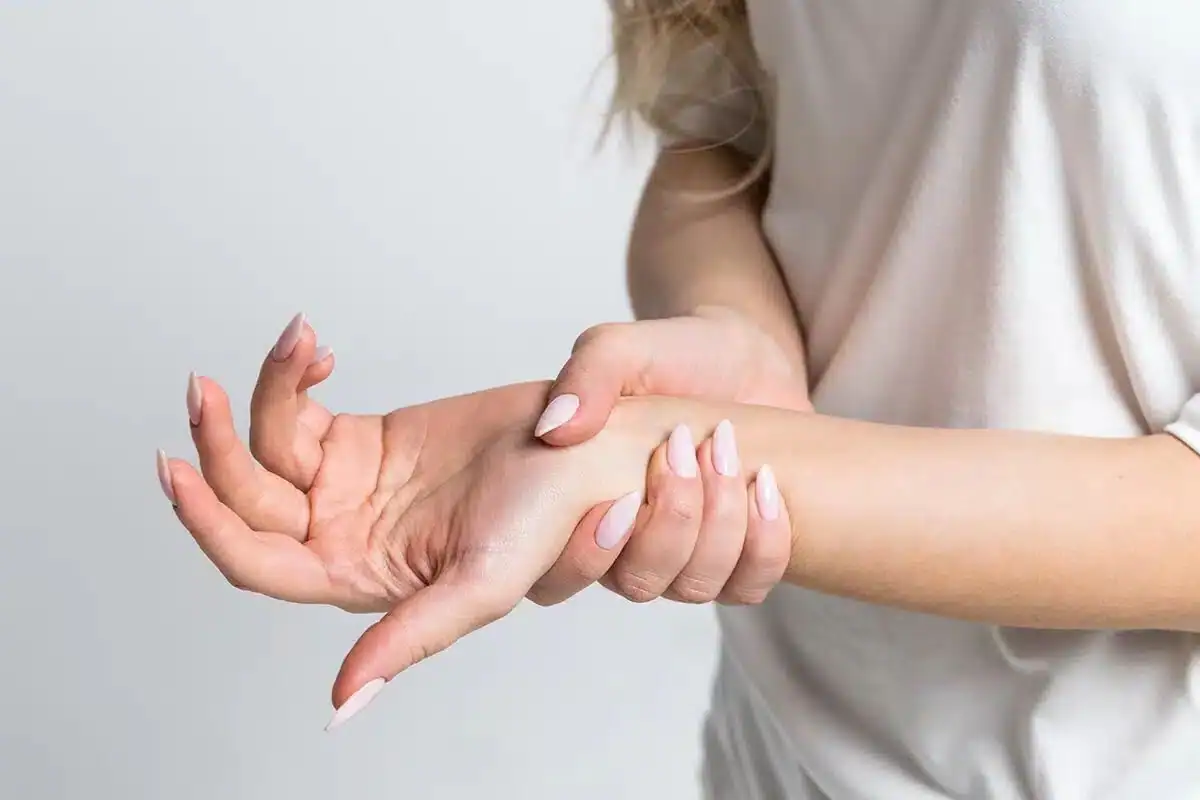
Peripheral Neuropathy
Recent studies suggest a connection between celiac disease and peripheral neuropathy. This neurological condition causes pain, numbness, and tingling, most commonly in the feet. Doctors do not yet understand the exact relationship between the two, but more than ten percent of people with celiac disease have this symptom.

Advertisement
Tooth Decay
Some celiac patients, most often children, have dental defects such as damage to tooth enamel and tooth discoloration. Children and adults with celiac disease can also develop ulcers in the mouth. Unfortunately, the tooth damage may be irreversible. Adopting a gluten-free diet may help prevent further deterioration but cannot undo existing damage.

Advertisement
Musculoskeletal Problems
Those with celiac disease often have musculoskeletal problems like joint pain and aching bones. Though it is not clear exactly how celiac disease affects the joints and bones, some suggest that malabsorption is the culprit. The nutrient deficiencies or autoimmune processes experienced by people with celiac disease may impact joint and bone health, thereby generating other health conditions beyond the gastrointestinal tract.
Advertisement
Menstrual Irregularities
In some cases, celiac disease can interfere with a woman's regular menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods, heavier than normal bleeding, or even amenorrhea—the full absence of menstruation. The exact mechanisms behind this connection are still being studied. Nevertheless, the link underscores the importance of considering celiac disease in the diagnostic process for unexplained menstrual irregularities.

Advertisement
Anxiety and Depression
While it may not be immediately apparent, celiac disease can also take a toll on mental health. Some individuals with this condition may experience unexplained anxiety, depression, or mood swings. The reasons behind this are multifaceted and may involve nutrient deficiencies, gut inflammation, or even the stress of living with a chronic autoimmune disease. Let's face it, living with celiac disease can create stress when grocery shopping, going out to eat with friends, visiting family for the holidays, or almost anytime there's a meal. Addressing the emotional aspect of celiac disease is crucial for overall well-being.

Advertisement
Unexplained Weight Loss
One of the more puzzling aspects of celiac disease is unexplained weight loss. Despite maintaining a seemingly healthy diet, individuals with undiagnosed celiac disease might find themselves losing weight. This is often due to the malabsorption of essential nutrients, which can lead to muscle wasting and a decrease in body mass. If you're experiencing unexplained weight loss, it's worth discussing the possibility of celiac disease with your healthcare provider. It could be one of several potential explanations.

Advertisement
Cognitive Impairment
In some cases, celiac disease can manifest with cognitive impairment, sometimes colloquially referred to as "brain fog." Individuals may experience difficulties with concentration, memory, and executive function. This cognitive cloudiness is thought to be related to the inflammation and nutritional deficiencies associated with celiac disease. A gluten-free diet may help improve cognitive function over time.

Advertisement
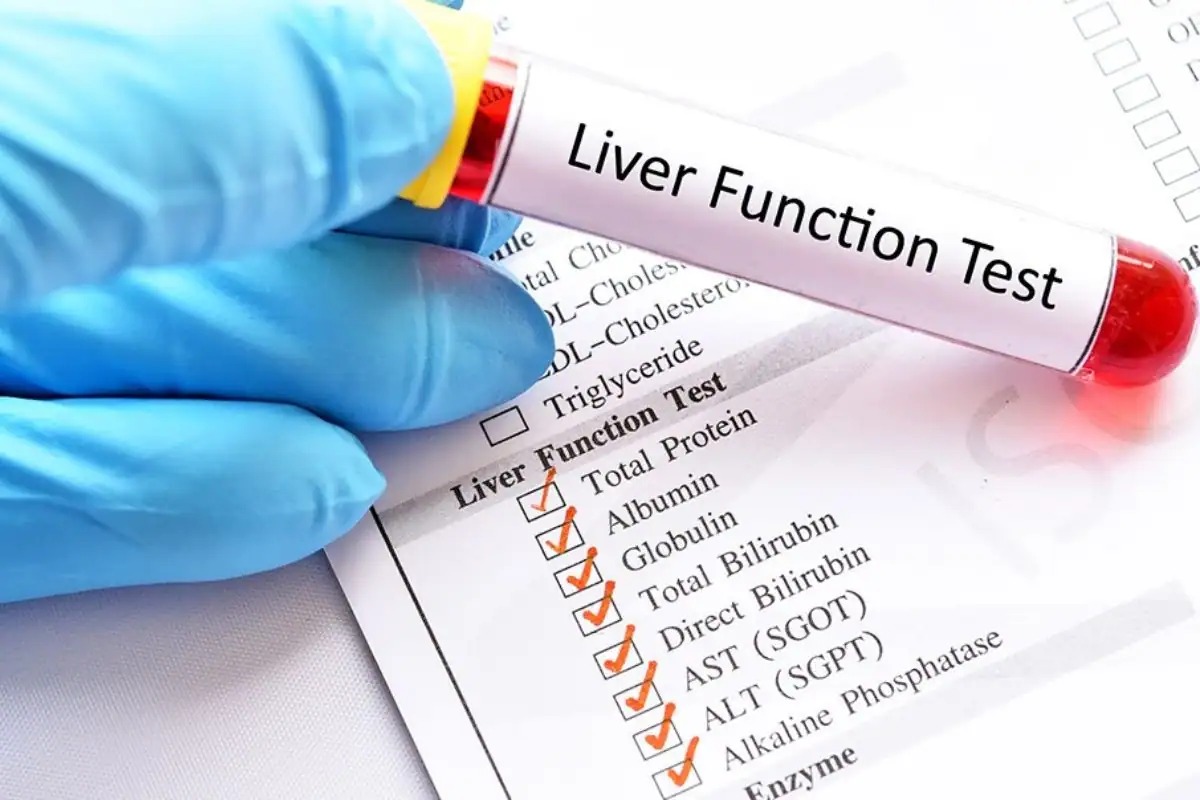
Elevated Liver Enzymes
Some individuals with celiac disease may exhibit elevated liver enzymes in blood tests that check liver function. This can indicate liver inflammation or injury, which is sometimes associated with the autoimmune response triggered by the ingestion of gluten. Therefore, monitoring liver function is crucial for individuals with celiac disease to prevent further liver damage and maintain their overall health.
.png)




